Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are the principles of Agile work?
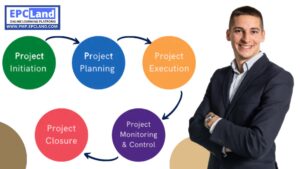
Agile is a framework and pragmatic way of thinking that helps you meet changing requirements. It focuses on achieving maximum return on business priorities within allowed time and budget, especially when the will to achieve outweighs the risks.
There are four principles commonly used to highlight the difference between agile and waterfall (or more traditional) approaches to project management.
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
In an Agile environment, project delivery methods are driven by teams that focus on core deliverables, iterate over time, and collaborate with end users.
Allowing users to drive project design greatly improves project outcomes.
Agile upholds advantage and innovation through collaboration with a particular focus on customer satisfaction, quality, teamwork, and effective management.
Don’t Miss the 1000+ MCQ questions & hundreds of quizzes on PMP Knowledge Areas and Various important sections.
Individuals and interaction over process and tools
Agile emphasizes a shift from control to consensus. We focus on people who create value through engaged, accountable, and high-performing teams with a focus on data sharing, openness, team communication, and learning from feedback.
This often requires a change in behaviour. Managers serve and lead inside and outside the team to create commitment and accountability towards the end goal.
Responding to change over following a structured plan
A traditional “waterfall” uses an agreed scope to create a schedule and resource plan. Agile establishes resources and time that ultimately determine scope. There are a series of time and cost delivery windows, sprints, during which the project evolves.
Agile environments establish a minimum viable product (MVP). Core project artifacts that trigger the start of delivery. This is subject to change as the project team recognizes other opportunities or benefits that become available during each sprint.
Prototyping/working solutions over comprehensive documentation
The team has MVPs who work together to develop the product. What they offer and how they deliver it.
The delivery team is “prepared” so that they can focus on solving the problem they are dealing with. The team constantly adjusts the product range.