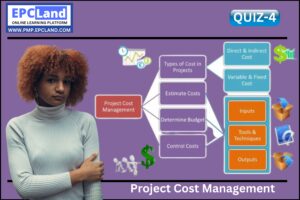
Project Cost Management is a crucial aspect of any project as it determines the success or failure of a project. It involves estimating, budgeting, and controlling costs throughout the project lifecycle. One of the key elements of Project Cost Management is controlling costs, which requires effective processes and strategies. Implementing these processes can help reduce expenses, increase efficiency, and improve project outcomes.
Cost control processes include identifying cost drivers, monitoring expenses, and tracking progress against budget. By staying vigilant and utilizing best practices in cost control, project managers can minimize waste and ensure the project stays within budget. However, it’s important to strike a balance between cost control and quality, as skimping on quality can negatively impact the end result. With the right cost control processes in place, project managers can achieve their goals, reduce costs, and deliver successful projects.”
What is the Importance of “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management
“Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management is important for several reasons:
- Budget Control: Effective cost control processes help in controlling and tracking project expenses, ensuring that the project stays within budget.
- Increased Efficiency: By reducing waste and streamlining processes, cost control leads to increased efficiency and improved project outcomes.
- Improved Decision Making: Through regular monitoring of expenses and progress, cost control processes provide valuable insights for informed decision-making.
- Risk Mitigation: By detecting cost overruns early and taking corrective action, cost control processes minimize the risk of cost overruns and project failures.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: By delivering the project within budget, cost control processes help to achieve stakeholder satisfaction and increase their confidence in future projects.
- Transparency and Accountability: Cost control processes provide transparency and accountability in the project, enabling project managers to justify expenses and demonstrate value to stakeholders.
Attempt Quiz-1 on Control Cost Process
What are Various Steps required in “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management
The steps involved in “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management include:
- Establish a Budget: Set a budget for the project and allocate resources accordingly.
- Monitor Expenses: Regularly monitor and track expenses to ensure that the project stays within budget.
- Identify Cost Drivers: Identify the key factors that drive project costs and prioritize them.
- Track Progress: Compare actual costs against the budget and track progress over time.
- Analyze Variances: Analyze the reasons for any variances between actual and planned costs.
- Implement Corrective Actions: Take corrective actions to address cost overruns and ensure that the project stays within budget.
- Review and Update Budget: Regularly review and update the project budget as required to reflect changes in scope or resources.
- Communicate with Stakeholders: Regularly communicate with stakeholders regarding the project’s cost performance and take their feedback into account.
- Continuously Improve: Continuously review and improve cost control processes to maximize efficiency and reduce waste.
What are various Tools & Techniques used for “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management
The following are the various Tools & Techniques used for “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management:
- Budgeting and Cost Management Software: Tools for creating and managing project budgets, tracking expenses, and generating reports.
- Earned Value Analysis (EVA): A method for measuring project performance by comparing actual work completed against planned work and budget.
- Variance Analysis: A technique for comparing actual results to planned results to identify and analyze variances.
- Activity-Based Costing (ABC): A method for allocating indirect costs to individual activities or products based on their consumption of resources.
- Cost of Quality (COQ): A technique for evaluating the cost of quality-related activities, such as inspections and testing.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis (CBA): A method for evaluating the costs and benefits of a project to determine its overall feasibility and value.
- Risk Management: A process for identifying, assessing, and mitigating project risks that could impact costs.
- Change Management: A process for managing and controlling changes to the project scope, budget, and schedule.
What are various Inputs required for “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management
The following are the various inputs required for “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management:
- Project Charter: The project charter provides the overall project context, including project goals, objectives, stakeholders, and constraints.
- Project Management Plan: The project management plan includes information on the project’s budget, schedule, resources, risk management plan, and change management plan.
- Budget and Cost Management Plan: The budget and cost management plan provides detailed information on the project’s budget, cost estimating methods, and cost control processes.
- Work Performance Data: Work performance data provides information on the actual costs of project activities and how they compare to the planned budget.
- Change Requests: Change requests provide information on requested changes to the project scope, budget, and schedule.
- Project Schedule: The project schedule provides information on the planned timeline for the project and the expected completion date.
- Risk Register: The risk register provides information on the project’s identified risks and how they could impact costs.
- Cost Forecasts: Cost forecasts provide information on expected costs for the project, including both direct and indirect costs.
What are various Outputs required for “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management
The following are the various outputs required for “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management:
- Cost Forecasts: Regular updates to the project’s cost forecasts, including both direct and indirect costs.
- Budget Updates: Regular updates to the project budget to reflect actual costs, planned costs, and any changes to the project scope or schedule.
- Change Requests: Approved change requests that impact the project’s budget, scope, or schedule.
- Cost Baseline: An approved cost baseline that serves as a reference for measuring project performance and controlling costs.
- Project Management Plan Updates: Regular updates to the project management plan, including the budget and cost management plan, risk management plan, and change management plan.
- Work Performance Information: Regular updates on work performance, including actual costs, progress against the schedule, and any variances from the plan.
- Cost Management Reports: Reports that provide information on the project’s cost performance, including actual costs, planned costs, and variances.
- Corrective Actions: Approved corrective actions to address cost overruns or other issues that impact the project’s cost performance.
What is Role of Project Manager in “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management
The role of the project manager in the “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management is crucial and can be summarized as follows:
- Developing the Budget and Cost Management Plan: The project manager is responsible for developing the project’s budget and cost management plan, including estimating costs, creating a cost baseline, and developing a cost control process.
- Tracking and Monitoring Costs: The project manager is responsible for tracking and monitoring project costs, including actual costs, planned costs, and variances, and updating the budget and cost management plan as needed.
- Managing Changes to the Project: The project manager is responsible for managing changes to the project, including changes to the scope, budget, and schedule, and ensuring that they are approved and reflected in the cost baseline and budget.
- Risk Management: The project manager is responsible for identifying and assessing project risks and taking appropriate actions to mitigate their impact on the project’s costs.
- Communication and Reporting: The project manager is responsible for communicating project cost information to stakeholders, including regular cost reports and updates on cost performance.
- Taking Corrective Actions: The project manager is responsible for taking corrective actions to address cost overruns or other issues that impact the project’s cost performance and ensuring that they are approved and reflected in the cost baseline and budget.
Attempt Quiz-2 on Control Cost Process
Final Take away on “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management
Control Costs Process is a crucial component of Project Cost Management and plays a key role in ensuring that projects are delivered within budget and to the desired quality level. The project manager, using inputs such as the project charter, project management plan, work performance data, and change requests, along with tools and techniques, tracks and monitors costs, manages changes, and takes corrective actions as needed to control costs. Effective cost control requires regular communication and reporting, as well as regular updates to the project budget, cost forecasts, and project management plan. The importance of controlling costs cannot be overstated, as it is critical to the success of any project.
FAQs on “Control Costs Process” in Project Cost Management
- What is the Control Costs Process in Project Cost Management?
- It is a process used to monitor the status of project costs and take corrective actions to stay within budget.
- What are the inputs of the Control Costs Process?
- Budget, Cost Performance Baseline, Performance Reports, Change Requests.
- What are the tools and techniques used in Control Costs Process?
- Earned Value Management, Forecasting, Variance Analysis.
- What are the outputs of the Control Costs Process?
- Cost Forecasts, Change Requests, Work Performance Information, Project Management Plan Updates.
- Why is the Control Costs Process important in Project Cost Management?
- It helps to ensure the project stays within budget, avoid cost overruns, and make informed decisions about changes to the project plan.