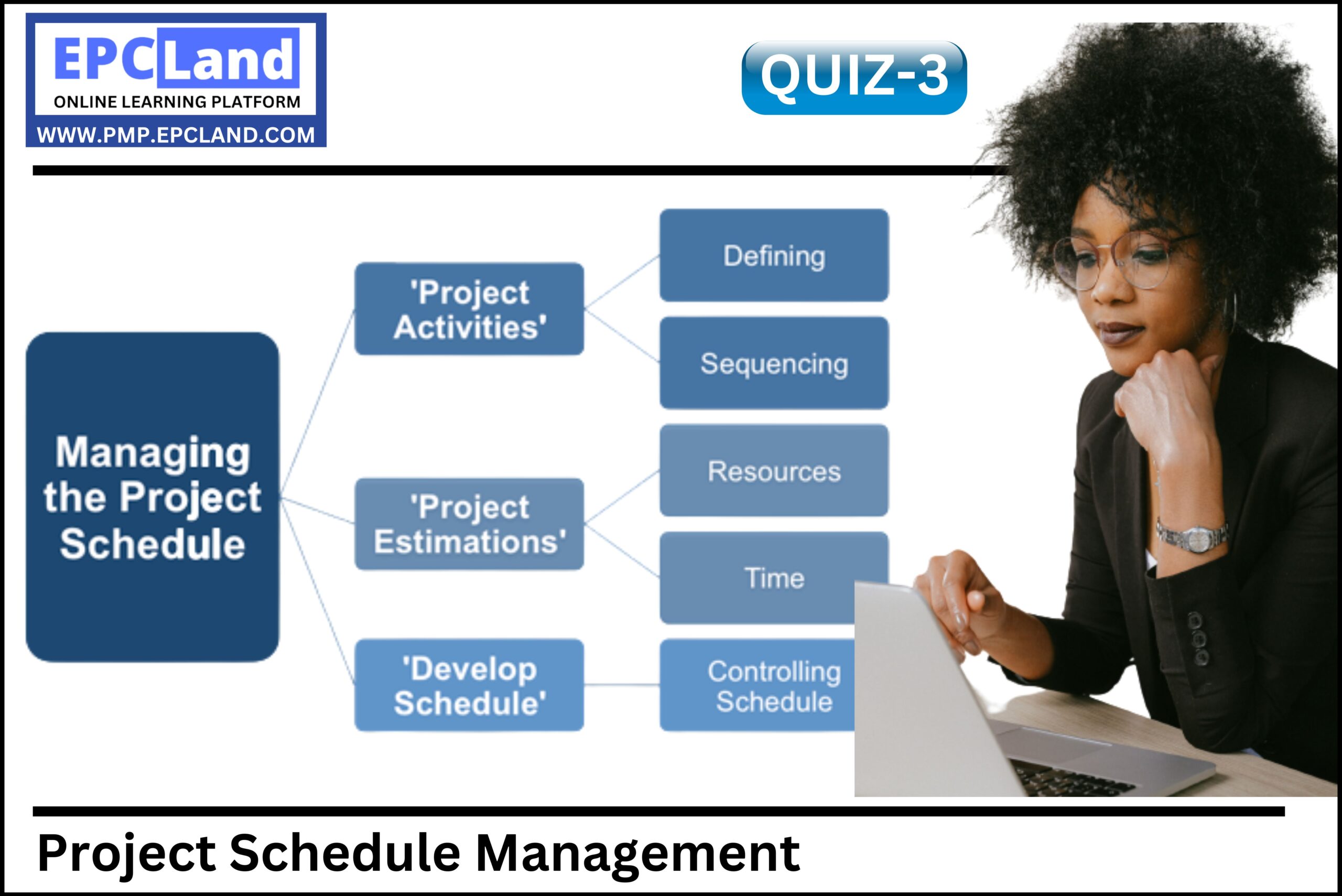
1.
A project manager looks at her schedule and sees that there has been a delay in completing a task. It seems practical to move a person from another task that is an expert on the work that is behind. There is a choice of using two different persons that are working on two different tasks. One person is working on a task that has five days of free float and the other is working on a task that has eight days of total float and no free float. Which person should be used to help out?
2.
Five tasks are scheduled to be completed in sequence. Each task has a finish-start relationship with the next task. Each has one day of total float. As of today, task one and two have been completed on schedule. How many days of float remain in the schedule for these tasks?
3.
The overall duration of the project schedule is not influenced by:
4.
Which of the following is considered to be a simulation technique?
5.
A task was scheduled to use two persons, full time, and take two weeks to complete. Instead, the project manager was only able to assign one person to this task. At the end of two weeks, the person assigned to the task was 75% complete. What is the cost performance index?
6.
The main difference between the two types (ADM, arrow diagramming method, and PDM, precedence diagramming method) of the critical path method (CPM) of scheduling is:
7.
Resource leveling will generally:
8.
The project schedule is not used to determine:
9.
A project manager is managing a project and is considering the reschedule of an activity because one of the project engineers must work on this activity and another activity at the same time. Each of the activities is scheduled to have a duration of two weeks. One of the activities is on the critical path and the other activity has eighteen days of free float. The project manager should:
10.
The program evaluation and review technique (PERT) method of scheduling differs from the critical path method (CPM) because the PERT method: