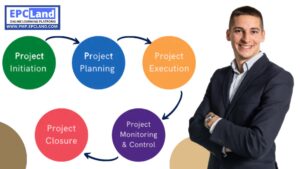
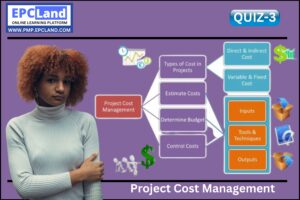
1.
You are working on a construction project that is running slightly behind schedule. You ask the team to put in a few extra hours on their shifts over the next few weeks to make up the time. To make sure everyone feels motivated to do the extra work, you set up a $1,500 bonus for everyone on the team who works the extra hours if the deadline is met. What kind of power are you using?
2.
Which of the following is an example of the “halo effect”?
3.
You are working in a matrix organization. You don’t have legitimate power over your team. Why?
4.
You are writing a performance assessment for your team. Which process are you in?
5.
Tina is a project manager who micromanages her team. She reviews every document they produce and watches when they come and go from the office. Which kind of manager is she?
6.
Tom is using an organization chart to figure out how he’ll staff his project. What process is he performing?
7.
Two team members are having an argument over priorities in your project. One thinks that you should write everything down before you start doing any work, while the other thinks you can do the work while you finish the documentation. You sit both of them down and listen to their argument. Then you decide that you will write most of it down first but will start doing the work when you are 80% done with the documentation. What conflict resolution technique are you using?
8.
Which of the following is NOT one of the top sources of conflict on projects?
9.
You’re a project manager on an industrial design project. You’ve set up a reward system, but you’re surprised to find out that the team is actually less motivated than before. You realize that it’s because your rewards are impossible to achieve, so the team doesn’t expect to ever get them. What motivational theory does this demonstrate?