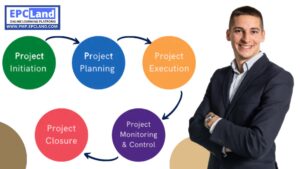
The Project Management Body of Knowledge Guide (PMBOK® Guide) established 10 project management knowledge bases as the foundation of the project management process and the root of the tree.
Understanding how the tree works requires understanding the roots and their functions, so understanding project management requires understanding these 10 knowledge areas. So the 10 knowledge areas of project management are:
Table of Contents
ToggleDont miss the Link Given to Each Knowledge area and Process Groups
Project Integration Management
This PMP knowledge area is characterized by the fact that there is one process in each of the five process groups. All project participants gather here to create the order of the project. Project integration management is the process of establishing and maintaining project team direction, goals, and scope management. Ensure that project changes are developed and implemented in accordance with the original goals and objectives of the project.
The integration management process is performed by the Project Integration Manager (PIM). He coordinates communications to ensure that project goals are clearly understood across organizational groups. He also ensures project goals, priorities, and timeframes are set and met.
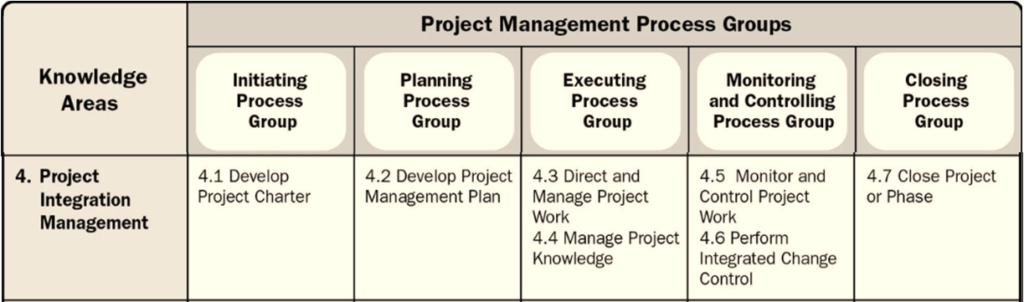
Out of 49 related PMP processes, this knowledge area has 7 of his processes, spread across all 5 process groups.
Project integration Management has seven processes included in it:
- Develop Project Charter
- Develop Project Management Plan
- Direct and Manage Project Work
- Manage Project Knowledge
- Monitor and Control Project Work
- Perform Integrated Change Control
- Close Project or Phase
Project Scope Management
The project scope must be clearly defined and adhered to throughout the project lifecycle. It is the project manager’s responsibility to define, measure, monitor, and manage the scope. Simply put, this means that you cannot go over budget or build something that has not been agreed upon in advance. Minimize and enable. For a project to be successful, the scope of the project should be as clear and complete as possible. If you don’t know what it is, you probably can’t manage it.
A project scope statement defines the purpose, deliverables, and limits that apply to those deliverables for a particular project. It also describes the environment in which this work takes place. A project scope statement is used to outline a project’s goals, requirements, and constraints (schedule and budget).
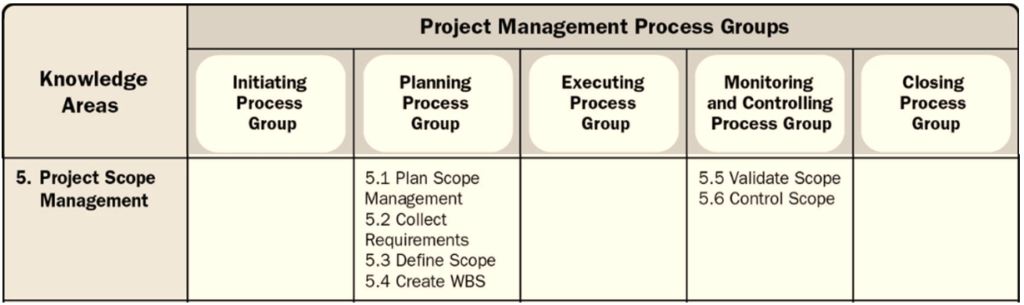
Six of it’s 49 relevant PMP processes are in this knowledge area, four of which fall under the Planning process group and two under the Monitoring and Control process group.
Project Scope Management includes six processes:
- Plan Scope Management
- Collect Requirements
- Define Scope
- Create WBS(Work Breakdown Structure)
- Validate Scope
- Control Scope
Project Schedule Management
Project managers who want to achieve great results need to focus on project planning. Deadline management is a key component of project management as it can optimize resources, reduce costs and improve project success.
In this PMP Knowledge Area you will learn how to create, update, monitor and analyze schedules. You’ll also learn how to meet schedules that are often overlooked by inexperienced project managers. Learn to calculate work hours and apply constraints, which are essential for accurate scheduling.
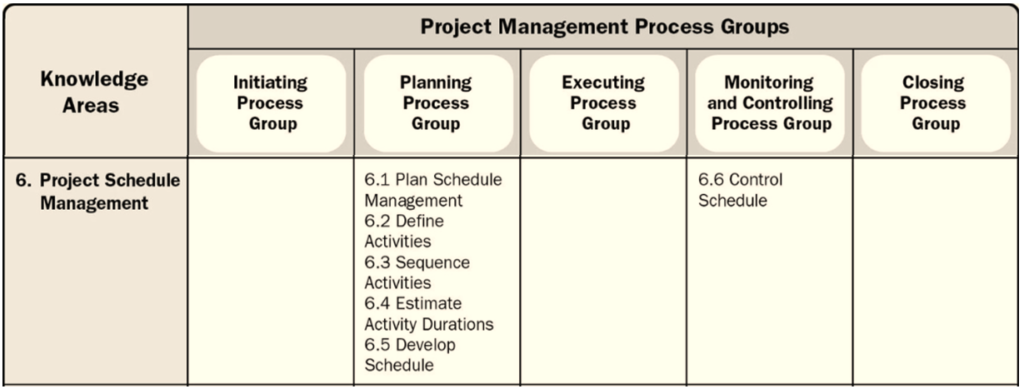
Schedule Management includes six processes:
- Plan Schedule Management
- Define Activities
- Sequence Activities
- Estimate Activity Duration
- Develop Schedule
- Control Schedule
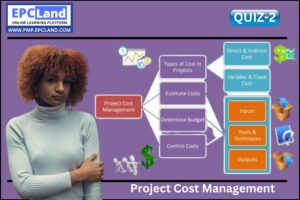
Project Cost Management
As with any organization, each project is assigned a budget. Whether you are pursuing a project management career at your current company or are considering pursuing it as a new career path, one of the most important things to understand about project management is: It’s how the costs fit into the equation.
Project cost management is about ensuring that both stakeholders and her members of the team know how much money is available for a particular project and what comes with it. This includes budgeting, estimating costs, and tracking actual spending. It’s also important to know the financial status of other projects you are working on or have successfully completed. This allows you to see if your organization can afford any additional projects that may arise.
It’s important to know how much each aspect of your project will cost so that you can properly budget for other future projects. Each project has different costs depending on its size, duration and complexity.
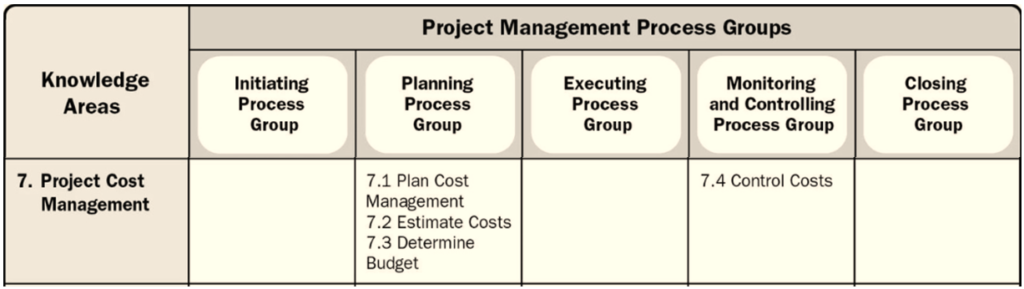
Out of 49 PMP processes, this PMP knowledge area has 4 of his processes divided into 2 process groups. Three of these fall under the Planning process group and one under the Monitoring and Control process group.
Project Cost Management includes four processes:
- Plan Cost Management
- Estimate Costs
- Determine Budget
- Control Costs
Project Quality Management
Here we carry out all the necessary activities to ensure the quality of the project. As such, we may be responsible for conducting formal and informal meetings. Developing quality plans; managing project documentation; establishing inter-project controls. The main project management principle behind this category is that projects can only achieve their goals if they are properly managed. The quality of the project itself therefore depends on this quality control process.
Project quality management (or quality control) is the process of measuring, analyzing, and improving the quality of projects, products, or services. Quality management focuses on implementing processes to meet customer needs and expectations, reduce waste and improve overall performance. Project quality management is typically implemented on targeted projects that must or can benefit from meeting certain quality criteria or objectives.
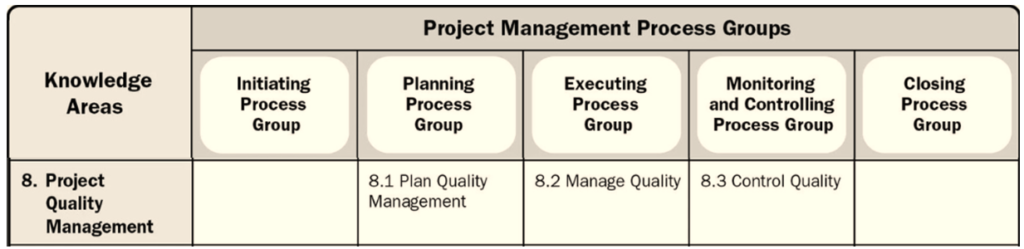
Of the 49 PMP processes, there are 3 in this knowledge area. There is one for each of the planning, execution, monitoring and control process groups.
Project Quality Management includes three processes:
- Plan Quality Management
- Manage Quality
- Control Quality
Project Resource Management
This phase ensures that these resources are properly allocated to each project activity. This includes ensuring that all required resources for each project activity are available, incorporating them into the project plan, and ensuring they are properly managed and monitored.
Develop a formal resource allocation plan within each project using scoping exercises and related tools. The purpose of this exercise is to clearly define project boundaries. This is especially true when resources within a project are assigned in the early planning stages without much consideration of their specific role in the overall scope of the project.
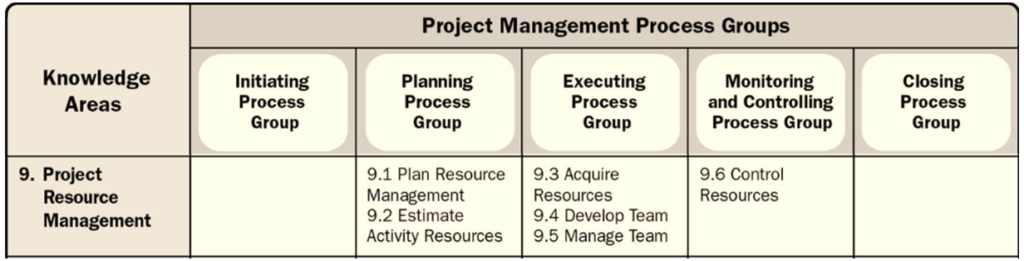
Of the 49 PMP processes, 6 are in this phase. They are categorized into three process groups: planning, execution, monitoring and control.
Project Resource Management includes six processes:
- Plan Resource Management
- Estimate Activity Resources
- Acquire Resources
- Develop Team
- Manage Team
- Control resources
Project Communications Management
The purpose of this process is to minimize potential negative impacts on the project. As a project manager, you must keep control over all internal and external communications related to your project. The project manager is responsible for managing stakeholder expectations and requirements based on their level of knowledge of the current state of the project. This means managing communications from internal and external stakeholders.
These stakeholders include clients, sponsors, change management teams, employees, customers, business her partners, subcontractors and the general public. You need to know which communication channel to use, such as: B. Email or Verbal Communications. Ensure that all communications meet the purpose of the communication.
PMP also focuses on preparing communication activities such as scheduling and facilitating meetings with managers and stakeholders to discuss issues that arise during the project.
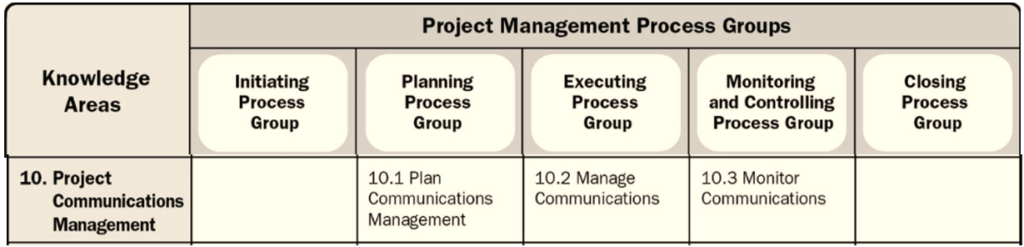
There are 3 of his 49 PMP processes, each corresponding to a planning, execution, and monitoring and control process group.
Project Communication Management includes three processes:
- Project Communication Management
- Manage Communications
- Monitor Communications
Project Risk Management
This knowledge area addresses everything you need to do to control risk. It is about identifying and evaluating risks, developing contingency plans to mitigate or avoid them, and managing the resulting risks. These include issues that can affect project completion dates, costs, quality, staffing levels, resource allocation, supplier financial health, customer satisfaction with services, and other external factors.
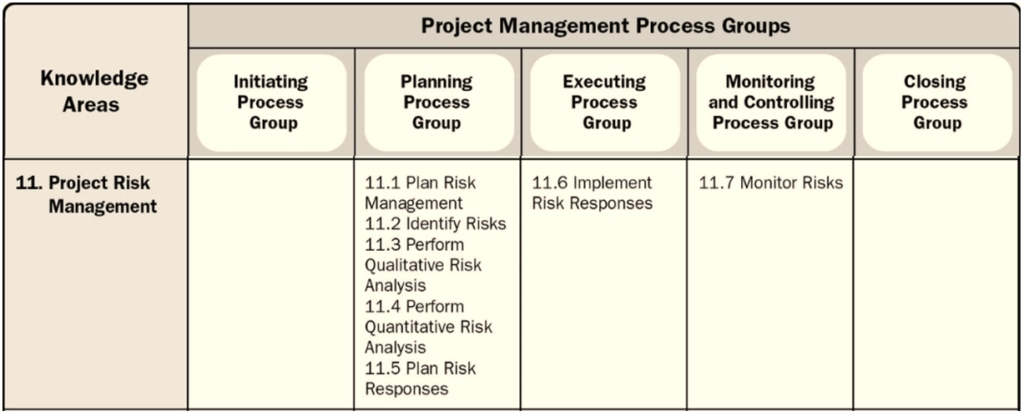
Out of 49 PMP processes, 7 are distributed across the planning, execution, and monitoring and control process groups.
Project Risk Management Process includes seven processes:
- Plan Risk Management
- Identify Risks
- Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis
- Perform Quantitative Risk Analysis
- Plan Risk Responses
- Implement Risk Responses
- Monitor Risks
Project Procurement Management
This knowledge area deals with the procurement of goods and services and the determination of who those suppliers are. We also manage contracts. The project manager is responsible for ensuring that the various components of the project are integrated into her single entity. This is accomplished by ensuring that her members of the team are aligned with project goals.
The Project Procurement Management knowledge area is concerned with procuring project goods and services, coordinating procurement activities, managing contractual matters related to delivery and supplier agreements, and ensuring compliance with company policies. Knowledge in this area is essential for project managers and is one of the most difficult areas to cover as procurement involves multiple variables.
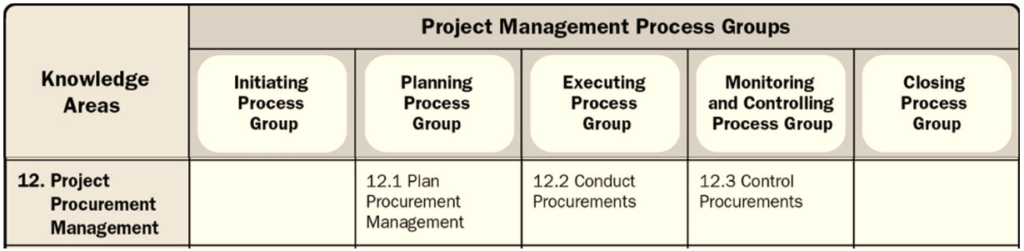
Of the 49 processes in PMP, there are 3: Plan, Execute, Monitor and Control.
Project Procurement Management includes three processes:
- Plan Procurement Management
- Conduct Procurements
- Control Procurements
Project Stakeholder Management
Ultimately, the success or failure of a project depends on handing it off to stakeholders.
Stakeholder management is the process of developing an organizational environment in which stakeholders are understood and met as they are most important to the success of a project. An organization’s project management plan defines stakeholders as those who have a legitimate interest in the project, including customers, business partners, managers, sponsors, and others who use or are affected by the results of the project. To do.
Stakeholder management is particularly important in project management insofar as the project manager’s responsibility begins with stakeholder selection. Unless this process is completed completely and accurately, it is unlikely that the right people will be identified for the project.
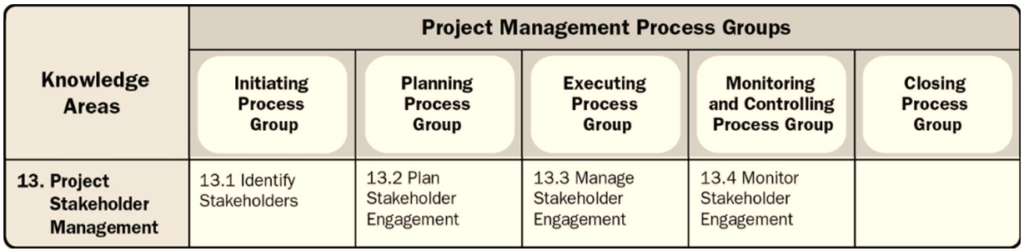
There are 4 of the pmp 49 processes that fall into this knowledge domain.
Project Stakeholder Management includes four processes:
- Identifying Stakeholders
- Plan Stakeholder Management
- Manage Stakeholder Management
- Monitor Stakeholder Engagement